BLOG
BLOG
Cast Iron vs. Aluminum Housing: Which Is Better for Rotary Tiller Gearboxes?
When choosing a rotary tiller gearbox, the material of the gearbox housing is a critical factor that directly affects performance, durability, heat management, and long-term maintenance. The housing is more than a shell—it maintains structural integrity, supports bearings, protects gears, and ensures stable power transmission during demanding tillage operations.
This article compares cast iron vs. aluminum gearbox housings to help OEMs, distributors, and industrial buyers select the right material for their agricultural gearbox applications.
Why Housing Material Matters
A gearbox housing affects:
- Strength and load capacity
- Vibration and noise levels
- Heat dissipation
- Corrosion resistance
- Overall weight and handling
- Cost and manufacturability
For a rotary tiller gearbox working under shock loads and continuous torque, choosing the correct material ensures longer service life and more stable operation.
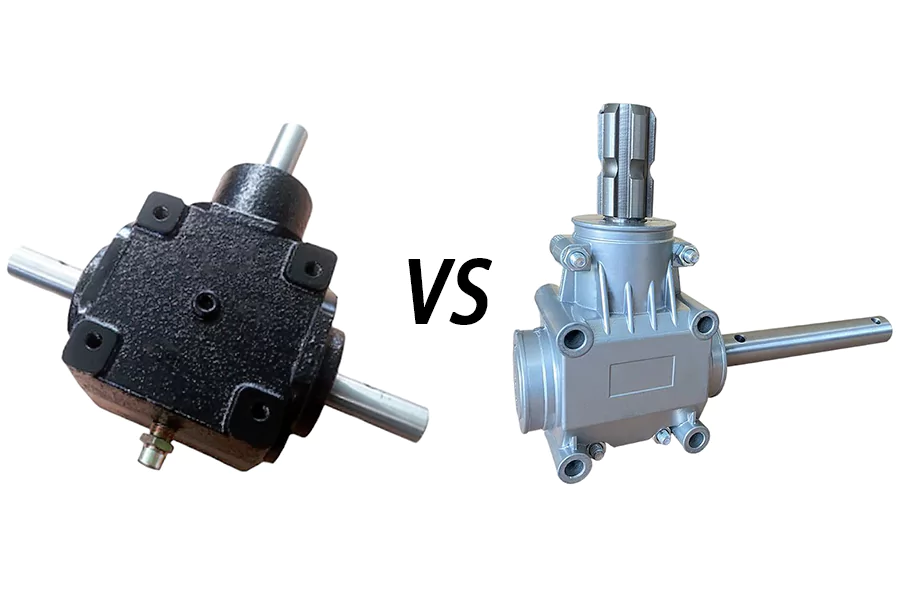
Cast Iron: The Heavy-Duty Workhorse
Pros
1. High Strength and Durability
Cast iron offers excellent compressive strength and rigidity, making it ideal for rotary tiller gearboxes exposed to heavy torque, rocky soil, and deep tilling operations. It maintains internal alignment well, even under repeated shock loads.
2. Superior Vibration Damping
Cast iron naturally absorbs vibration better than most metals. This reduces noise, minimizes stress on gears and bearings, and extends the overall life of the gearbox.
3. Strong Heat Resistance
Under long working periods, cast iron remains dimensionally stable. It does not warp easily at high temperatures, ensuring consistent gear meshing and reliable performance.
4. Cost-Effective Manufacturing
For large and heavy housings, cast iron casting processes are often more economical, making cast-iron gearboxes generally more affordable at the initial purchase.
Cons
1. Heavy Weight
Cast iron is significantly heavier than aluminum. This increases the overall weight of the tiller and makes the gearbox more difficult to handle during maintenance or installation.
2. Susceptible to Corrosion
If the protective coating is scratched or damaged, cast iron can rust in humid or wet environments. Proper finishing and repainting are essential for longevity.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Pros
1. Lightweight Construction
Aluminum housings greatly reduce total machine weight, making rotary tillers easier to operate, transport, and mount. This is especially advantageous for smaller tractors or walk-behind tillers.
2. Natural Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum forms a protective oxide layer, providing good resistance to corrosion. This makes aluminum housings suitable for moist, coastal, or high-humidity environments.
3. Excellent Heat Dissipation
Aluminum transfers heat efficiently, helping the gearbox cool faster during continuous work. This can reduce overheating issues and protect internal components in specific operating conditions.
Cons
1. Lower Strength
Aluminum is not as strong as cast iron, especially under sudden shock loads. For heavier applications, the housing might need to be thicker or reinforced, which increases size and cost.
2. Higher Manufacturing Cost
High-quality aluminum castings can be more expensive to produce, often resulting in a higher initial cost for aluminum gearboxes.
3. Larger Housing Size
To achieve similar strength to cast iron, aluminum housings may require more material, resulting in a bulkier design. This could affect implement layout or mounting dimensions.
Which Should You Choose?
Choose Cast Iron If:
Your rotary tiller gearbox will undergo heavy-duty, high-torque work.
The machine frequently encounters rocky soil or deep tillage.
You want maximum vibration damping and long-term structural stability.
Additional weight is not a concern for your tractor or equipment.
Choose Aluminum If:
- You prioritize a lightweight tiller for easier operation and transport.
- Your application involves light to medium soil conditions.
- Corrosion resistance is important (wet, coastal, or humid regions).
- Heat dissipation is a priority for your operating environment.
Conclusion
Both materials perform well, but each serves different operational needs. Cast iron offers unmatched strength and vibration control for heavy-duty rotary tiller gearbox applications, while aluminum provides lightweight handling, improved corrosion resistance, and better heat dissipation for lighter-duty use.
REQUEST A QUOTE
OR GET MORE
INFORMATION
Leave us a message. We will contact within 12 hours.